
Every delayed roll-out of new features or patches has a hidden cost: lost opportunities, frustrated users, and reduced growth. A CI/CD pipeline — the automated process to move code from dev to production — dictates how fast your business can change and deliver value. And if you're trying to optimize your CI/CD pipeline for faster delivery, speed is no longer just a measure of efficiency; it's a measure of competitiveness. Speed is no longer a measure of efficiency; it's a measure of competitiveness.
As a full-cycle software development agency, the Stfalcon team has firsthand experience implementing and perfecting scalable DevOps solutions. What we will illustrate here is how to accelerate the deployment process using best practices for continuous integration, proper tools, and lessons learned from actual projects in order to deploy rapidly without sacrificing quality or security.
Why Your Current Pipeline Might Be Slowing You Down
If your deployments are a grind rather than a sprint, it's a clear sign that your CI/CD pipeline needs proper CI/CD pipeline optimization. High-performing systems aren’t a coincidence — they're the result of eliminating common bottlenecks and continuously refining delivery workflows. Does your configuration involve any of these telltale indicators?
- Long build & test times. Do you perform all tests, all the time? A monolithic test suite can turn a quick commit into a long wait if unit tests, integration tests, and end-to-end (E2E) tests are executed in sequence.
- Redundant & sequential Jobs. Running tasks one after another instead of in parallel adds unnecessary wait time.
- Inefficient caching. Every build should not start from scratch. A lack of proper caching for dependencies, build artifacts, and Docker layers means wasted time and compute resources.
- Unnecessary steps for small changes. Minor updates shouldn’t trigger the full deployment process.
- Lack of clear separation between staging and production. Without distinct environments, teams risk longer approvals and higher rollback costs.
- Excessive overhead. A pipeline bogged down by too many tools, complex configurations, or manual approvals (e.g., waiting for someone to click "approve" on every single deployment) is no longer a streamlined process; it’s a bureaucracy.
Struggling with slow CI/CD pipelines?
Let’s improve your workflow, remove bottlenecks, and make deployments faster.
Alina
Client Manager

Best Practices for Optimizing Your CI/CD Pipeline: 2025 Edition
Once you’ve identified inefficiencies in your pipeline, the next step is applying the right CI pipeline optimization techniques to address them. Here are the best practices our team uses to speed up deployments without compromising quality or security:
Keep It Modular & Maintainable
A well-structured pipeline is easy to read, debug, and reuse. Instead of one giant script, think of your pipeline as a series of connected, independent jobs.
- Utilize reusable pipeline templates to maintain project consistency.
- Establish distinct, well-defined stages for each task (e.g., build, test, deploy, monitor).
Accelerate the Build Process
Keep artifact creation time to a bare minimum. Each second matters, particularly with high-frequency commits. Use build caching for dependencies and Docker layers to prevent redoing from scratch.
- Build just what's changed, using monorepo tools or incremental builds.
- Use light containers and small base images to keep build times and attack surface low.
Optimize Testing
To truly optimize tests for CI, you need to ensure that testing works as a quality gate — not a bottleneck. The key is running the right tests at the right time.
- Parallelize test jobs to run multiple tasks simultaneously.
- Organize your tests and run them in a logical order (quick unit tests first, slow E2E tests later).
- Use test selection smarts to run only the affected tests for small, localized changes.
Automate Smart Deployment Flows
Manual intervention is defective and causes delays. An ideal CI/CD pipeline is self-healing and resilient.
- Use conditional logic to skip unnecessary steps, like a full deployment for a small documentation update.
- Automate rollbacks on failed deploys to quickly recover a functioning environment.
- Apply advanced deployment strategies like blue-green or canary deployments to limit risk and downtime.
Don’t Trade Speed for Security
Security must be an embedded part of your pipeline, not an afterthought obstacle.
- Bake security scanning into the pipeline with tools like Snyk.
- Lock down the pipeline itself using role-based permissions, audit trails, and artifact integrity checks.
Monitor & Improve Continuously
The fastest pipelines are always being scrutinized and optimized.
- Track key performance metrics (KPIs) like build time, test time, and failure rates through dashboards.
- Establish benchmarks and improvement targets, then celebrate when you hit them.
- Gather feedback from your developers on a regular basis to identify new areas of pain and opportunity for automation.
The best CI/CD pipelines in 2025 are not just fast — they're stable, secure, and scalable with your product and team. And though best practices are the foundation, the tools you choose can either rescue or ruin your pipeline's performance. So let's take a look at the technologies that power today's high-performing pipelines.
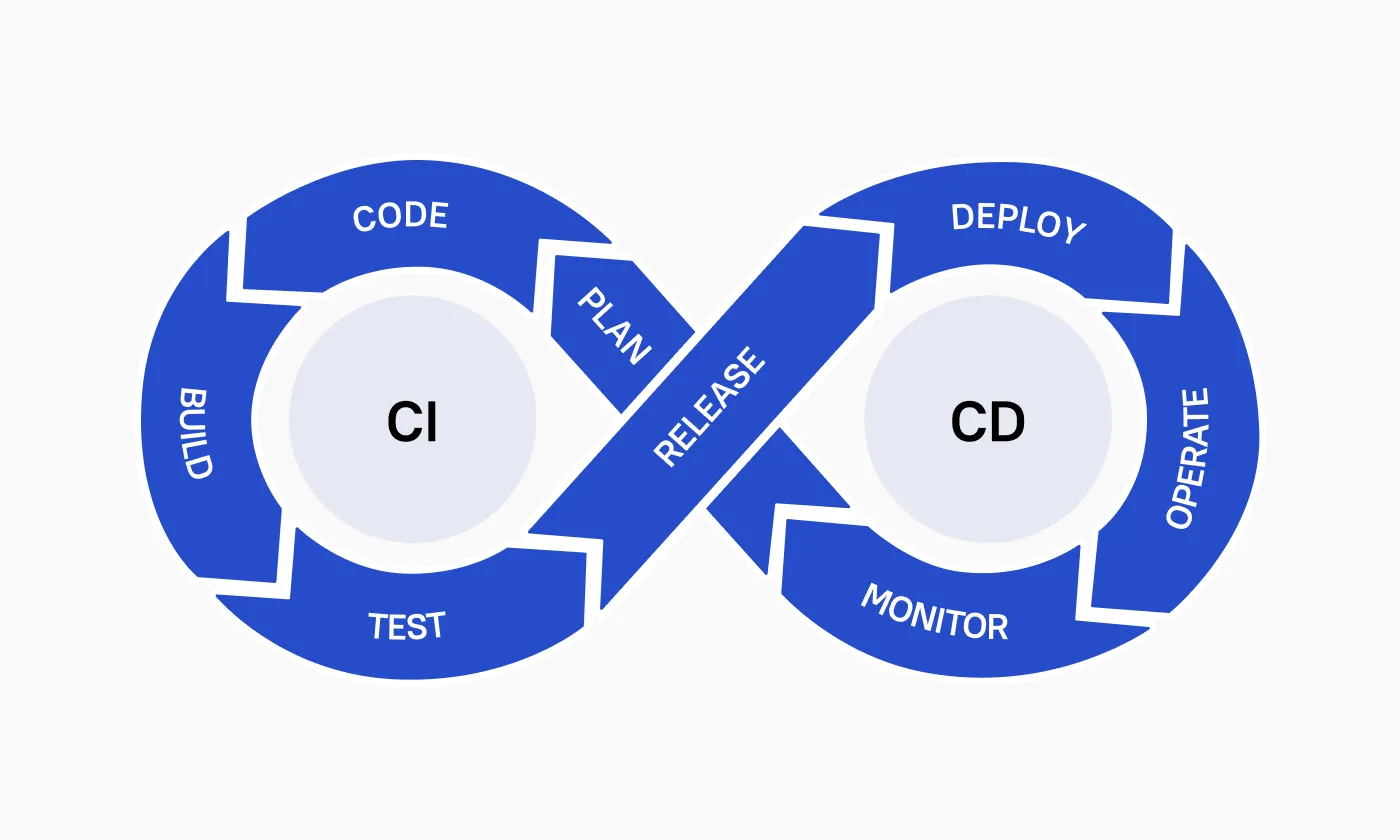
Choosing the Right Tools for Your Ideal CI/CD Pipeline
Selecting the appropriate tools to create your optimized pipeline comes next after mastering the basics. There is no "one-size-fits-all" approach to CI/CD web development. Your unique requirements and limitations will determine which toolchain is best for your team.
Factors to Consider
- Integration into the ecosystem and the current tech stack. To what extent does the tool interface with your existing cloud provider, version control system, and other services?
- Requirements for scalability and performance. Will the tool grow with your team, handle complex projects, and increase build volume without affecting performance?
- Team expertise and learning curve. Does your team already have some familiarity with a tool, or will they learn one?
- Hosting model (cloud-native vs. self-hosted). Do you require the flexibility and independence of self-hosting or a service that manages infrastructure for you?
- Implications for cost. What are the cost models, and how do you scale based on usage?
- Community support and extensibility. Is there a large community and an economy of plugins that can help you debug issues and extend functionality?
Popular Tool Categories
Despite the size of the CI/CD environment, the majority of tools can be divided into a few broad categories.
All-in-One Platforms: Stand-alone, comprehensive solutions that incorporate CI/CD, source code management, and other features.
Orchestration engines are tools for managing and executing pipeline jobs with dedication.
Deployment Tools: Advanced tools for deployment strategies, such as progressive delivery and GitOps.
Security Tools: Solutions that embed security scanning and checks directly into the pipeline.
IaC Tools (Infrastructure as Code): Tools for provisioning and managing infrastructure as part of your pipeline.
The ideal combination will depend on your business needs: whether that's speed, compliance, scalability, or CI/CD pipeline cost optimization.
Common CI/CD Optimization Pitfalls to Avoid
As you tune your pipeline, avoid falling into these common CI/CD web development pitfalls that will hold you back. The top teams avoid them by building a culture of ongoing improvement, not by way of new tools.
Manual Steps
Any human-interaction step in your pipeline can be a potential source of failure, delay, and variation. From approvals to config updates, these activities break the automation loop and slow down delivery.
Flaky Tests
Nothing erodes trust in a pipeline faster than a test that succeeds today but fails tomorrow without altering code. Flaky tests are the source of continuous noise, leading developers to re-run builds or bypass important checks, potentially shipping bad code to production.
Monolithic Pipelines
Having one really complex file pipeline is a pain to work with. It's difficult to debug when things are wrong and difficult to modify or update for other projects. Break huge pipelines into smaller, bite-sized jobs and templates.
Ignoring Security
Security tends to be an afterthought, "shifted right" to the downstream stages of the pipeline or even to production. By doing it last, you're building technical debt and creating vulnerabilities more expensive and time-consuming to fix. DevSecOps embeds security right from the start.
Lack of Monitoring
You can't see bottlenecks or even gauge the effect of your optimizations if you're driving blindly without dashboards or metrics. You can't measure what you can't fix. To observe and make data-driven decisions, keep an eye on important metrics like build time, test time, and deployments.
Neglecting Culture
Excellent pipelines are more than just tools. Your shiny new pipeline will fail if your developers aren't committed to it and if there isn't a collaborative and ownership culture. Establish a culture in which developers and operations teams are on the same page, share accountability, and have the ability to make improvements.
Avoiding these pitfalls ensures that as your product expands, your pipeline remains not only quick but also robust, safe, and sustainable.
Conclusion
A well-structured CI/CD pipeline is not just an engineering advantage — it's a business enablement, a driver for quick releases, and higher product quality. By minimizing delays, automating smartly, and adding security and monitoring at every stage, your pipeline is a competitive advantage and not a bottleneck.
But building and maintaining the best CI/CD pipeline is not a one-and-done project. It's an improvement journey — continually refining builds, adopting new practices, and synchronizing your tools and team culture for growth. And if you’re focused on fixing slow deployment pipelines, the path starts with identifying bottlenecks and rebuilding processes that truly support scale and speed.
Ready to change the game with software delivery? As a full-cycle software development company, we specialize in creating, deploying, and optimizing best-in-class CI/CD pipelines tailored to your unique requirements. Reach out to us today for a consultation!
FAQ About CI/CD Pipeline Optimization
How quickly can a CI/CD pipeline be installed or upgraded?
Project complexity will dictate timelines, but a lightweight pipeline can typically be installed within days, and an enterprise-level heavy-duty pipeline will take weeks. The secret is to begin small and continually get better.
How are Continuous Integration, Continuous Delivery, and Continuous Deployment different?
Implementing Continuous Integration (CI) means merging and testing code changes on a regular basis. Continuous Delivery (CD) is keeping the codebase in a state of readiness to be released. Continuous Deployment (CD) is about automatically deploying all changes to production after they've passed all checks.
How do I measure the success of my CI/CD pipeline?
Metrics like build time, test coverage, deployment rate, mean time to recover (MTTR), and failure rates are good ones to track. Trends in these show whether your pipeline is speeding up delivery without sacrificing quality.
Do small teams or startups really need a CI/CD pipeline?
Yes — even a basic pipeline saves time with automated testing and deploys. For startups, it lets them iterate faster and sidestep costly errors when scaling.



