Computerized clinical decision support systems, known as CDSS, signify a profound transformation in modern healthcare. These systems are designed to enhance and support clinicians in their intricate decision-making processes. Since their initial adoption in the 1980s, CDSS has undergone rapid evolution. They are now predominantly integrated into electronic medical records and various computerized clinical workflows, facilitated by the increasing global adoption of advanced electronic medical records. Even so, despite these advancements, several uncertainties persist regarding the impact of CDSS on healthcare providers, patient outcomes, and associated costs. While the past decades have witnessed numerous success stories in CDSS implementation, significant setbacks have also underscored the inherent risks. In this paper, we present a state-of-the-art overview of the application of clinical decision support systems in medicine, encompassing various types, current use cases with established effectiveness, common challenges, and potential drawbacks.
What is a Clinical Decision Support System?
A clinical decision support system (CDSS) is an application designed to analyze data with the aim of aiding healthcare providers in making informed decisions and enhancing patient care. It is a specialized form of the broader decision support system (DSS) commonly employed in business management. The primary focus of a CDSS is to leverage knowledge management for providing clinical guidance based on various facets of patient-related information. These systems facilitate integrated workflows, offer real-time assistance during care delivery, and provide recommendations for care plans.
In the context of clinical decision support systems, data mining is often employed to examine a patient's medical history alongside pertinent clinical research. This analysis aids in anticipating potential events, such as drug interactions or the identification of disease symptoms.
Want a web app that does more?
Let's build a solution that's smart, sleek, and powerful.
Alina
Client Manager

Classification of Clinical Decision Support System
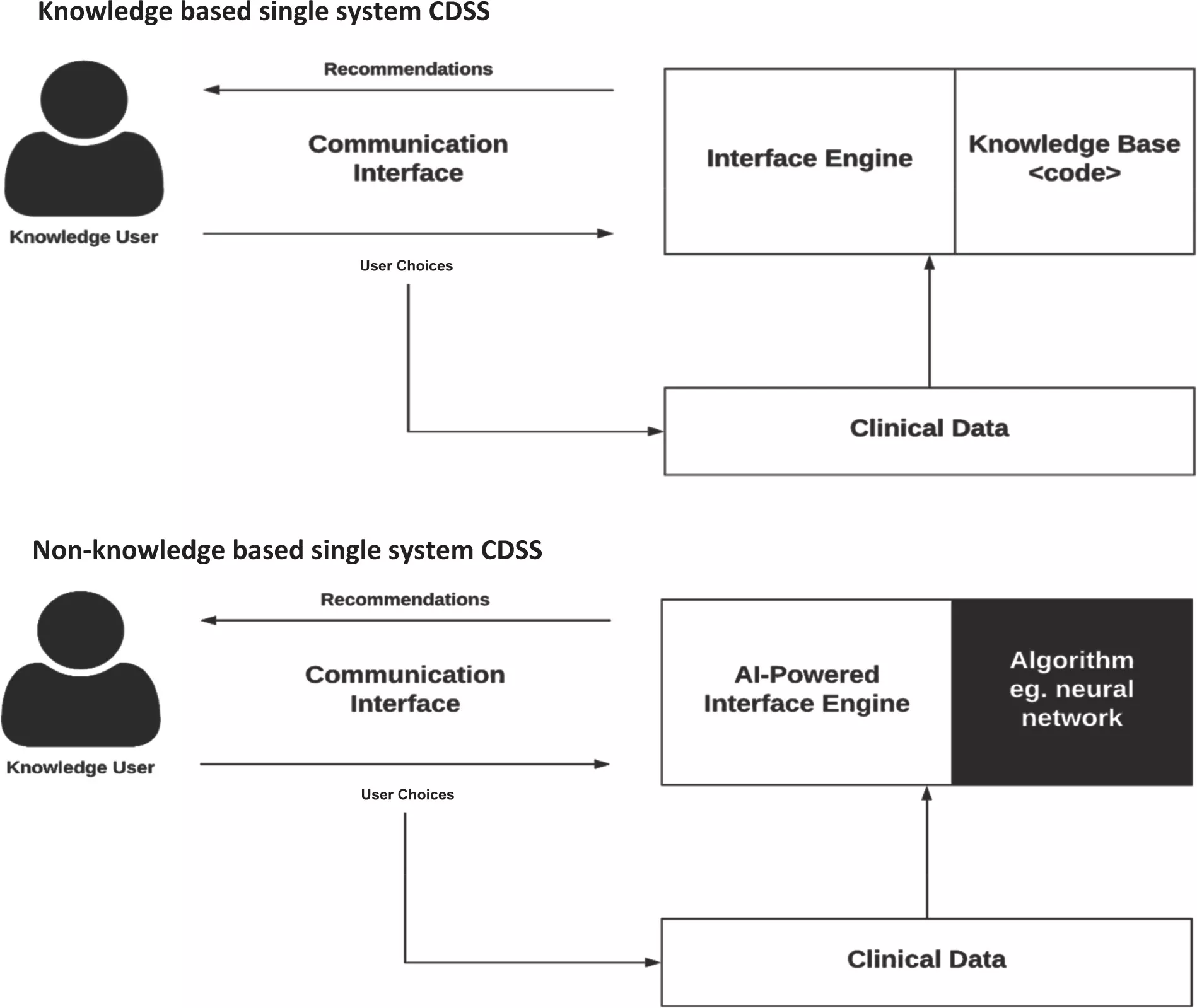
CDSSs have been categorized into various types and classifications, considering intervention timing and whether their delivery is active or passive. These systems are commonly classified into two main categories: knowledge-based and non-knowledge-based.
In knowledge-based CDSS, rules are formulated, typically in the form of IF-THEN statements. The system retrieves relevant data, assesses these rules, and generates an appropriate action or output. These rules can be established based on literature-derived, practice-based, or patient-specific evidence.
On the other hand, non-knowledge-based CDSS still rely on data sources, but they leverage technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), machine learning (ML), or statistical pattern recognition to make decisions, rather than being explicitly programmed with expert medical knowledge. This category represents a rapidly expanding use case for AI in medicine, although it comes with challenges. These challenges include understanding the rationale behind AI-generated recommendations (commonly referred to as "black boxes") and issues related to data availability. As of now, non-knowledge-based CDSS has yet to achieve widespread implementation. Both knowledge-based and non-knowledge-based CDSS share common components, albeit with subtle distinctions.
The Purpose of Clinical Decision Support Systems (CDSS)
The primary objective of a clinical decision support system is to aid healthcare providers in analyzing patient data and utilizing this information to assist in making accurate diagnoses. CDSSs offer valuable information to clinicians and primary care providers, with the overarching goal of enhancing the quality of care provided to their patients.
CDSS tools serve various functions, such as providing reminders for preventive care, issuing alerts regarding potential drug interactions that could pose risks, and notifying clinicians about scheduled redundant tests for their patients. By doing so, using a CDSS can lead to cost reduction and increased operational efficiency within healthcare settings.
Furthermore, some healthcare providers deploy CDSSs to identify cases where patients may have received incorrect diagnoses or been prescribed incorrect medication dosages. Such errors are flagged and added to problem lists, and this data is incorporated into population health management (PHM) reports. These reports, in turn, serve as the foundation for quality improvement initiatives in healthcare.
What Advantages Does Clinical Decision Support Offer?
When evaluating clinical support decision systems, it's crucial to consider both the pros and cons. Here are some benefits associated with clinical decision support systems (CDSS):
- Minimization of Medication Errors: CDSS helps reduce the likelihood of medication errors by providing timely and accurate information about drug interactions, dosages, and contraindications.
- Centralized Information Repository: Acting as a central repository, CDSS consolidates all relevant information, ensuring healthcare professionals have comprehensive data at their fingertips.
- Reduced Risks of Misdiagnosis: By offering insights and recommendations based on available data, CDSS contributes to lowering the risks of misdiagnosis, and improving diagnostic accuracy.
- Consistent Information Delivery: CDSS ensures the consistent and reliable delivery of information to the entire healthcare team, promoting standardized practices and enhancing collaboration.
- Enhanced Efficiency: Healthcare practitioners benefit from increased efficiency as CDSS streamlines decision-making processes, allowing for quicker and more informed responses.
- Improved Healthcare Service Quality: The use of CDSS contributes to the overall improvement of healthcare services by supporting evidence-based decision-making and adherence to best practices.
While these advantages are notable, it's essential to acknowledge the challenges associated with implementing CDSS. Integration into complex clinical workflows, potential interoperability issues with other software, and the constant influx of new medical data that may not be promptly incorporated pose significant hurdles. Additionally, the substantial volume of data integrated into existing systems may strain application and infrastructure maintenance. Understanding both the benefits and challenges is crucial for making informed decisions about the adoption of clinical decision support systems.
Use Cases and Industry Requirements for Clinical Decision Support
Clinical decision support (CDS) systems offer versatile applications across the healthcare industry, significantly impacting patient care. These systems play a crucial role in virus detection, personalized cancer therapies, and various aspects of medical treatment. Below are notable examples illustrating the use cases and applications of clinical decision support across different institutions:
Reducing Sepsis Mortality Rate
A hospital in Alabama implemented a computerized surveillance algorithm, resulting in a 50% reduction in sepsis mortality. Real-time analytics provided timely alerts for sepsis diagnosis and reminders for optimal treatment.
Specialized Support for Nurses at Mayo Clinic
Mayo Clinic is developing a specialized clinical decision support system for nurses to conduct precise phone screenings for patients seeking advice or appointments. Standardized questions ensure comprehensive patient information.
Genetic Testing and Emergency Department Visits
Harding University, in collaboration with Unity Health-White County Medical Center, found that combining CDSS with genetic testing data reduced emergency department visits by over 40% and hospital readmissions by over 50%.
Head Injury Guidance at Yale and Mayo Clinic
Yale and Mayo Clinic developed a CDSS application for patients with head injuries, adhering to industry guidelines. The system significantly reduced unnecessary CT scans by providing tailored treatment recommendations.
Reducing Unnecessary Lab Tests at the Department of Veteran Affairs
Clinical decision support tools implemented at the Department of Veteran Affairs in Indiana reduced unnecessary lab tests by over 11%, saving patients up to $150,000 without compromising healthcare quality.
In addition to these successful examples, clinical decision support systems offer various other benefits, including:
- Calculating drug dosages.
- Identifying reportable conditions through electronic health record (EHR) analysis.
- Evaluating drug formulation guidelines.
- Initiating automated reminders for medication or appointments.
- Analyzing severity indexes for diseases to suggest treatments.
- Moreover, machine learning and artificial intelligence are increasingly integrated into CDSS, showcasing their power in healthcare analytics. Notable achievements include lowering sepsis detection time by 12 hours and generating hourly predictions for ICU patients using deep learning tools.
As the healthcare industry continues to leverage advanced analytics techniques, the benefits of clinical decision support systems become increasingly evident. These systems, powered by machine learning and artificial intelligence, prove to be essential tools in delivering high-quality healthcare services. The examples provided underscore the importance and effectiveness of incorporating clinical decision support systems into the field of medicine.
How to Develop a Clinical Decision Support System
Building a clinical decision support system (CDSS) is crucial for modern healthcare facilities and practitioners. CDSS plays a pivotal role in optimizing care delivery by managing high volumes of data, minimizing repetitive testing, and enhancing patient safety. The system is designed to prevent errors, complications, and readmissions, showcasing its significance in healthcare. CDSS tools and examples in healthcare demonstrate its capability to sort and deliver digital information promptly.
Here's a guide on how to build a clinical decision support system:
Understand the Types of CDSS
CDSS systems fall into two broad categories: knowledge-based systems and non-knowledge-based systems. Knowledge-based systems define rules for data extraction and rule evaluation, while non-knowledge-based systems leverage machine learning and artificial intelligence.
Scope of Functions
CDSS performs various functions, including drug prescription, diagnostics, disease treatment, notification systems, and drug dispensing. These functions translate into reports and workflow tools, contributing to patient safety, cost reduction, clinical management, and streamlined administrative activities.
Data and Knowledge Integration
Utilize patient data and medical knowledge, storing them in the inference engine. This engine, when prompted, provides case-specific information and suggestions. Ensure seamless integration into existing IT infrastructure.
User Interface Design
Design the CDSS as a desktop or web application, or even experiment with a mobile app. The goal is to create a user-friendly interface that facilitates easy access to information and recommendations.
Interoperability
Ensure compatibility and interoperability with other healthcare systems and databases. This seamless integration enables efficient data management and accessibility for accurate diagnosis and improved healthcare services.
Implementation
Integrate CDSS into the healthcare facility's existing technology infrastructure. This process should be smooth and not disrupt daily operations.
Testing and Optimization
Conduct thorough testing to ensure the CDSS functions accurately and efficiently. Optimize the system based on feedback and performance evaluations.
Training and Adoption
Provide training to healthcare professionals for effective utilization of the CDSS. Encourage widespread adoption to maximize the system's benefits.
In conclusion, developing a clinical decision support system involves understanding the types of CDSS, defining its scope of functions, integrating data and knowledge, designing a user-friendly interface, ensuring interoperability, implementing the system, testing, optimizing, and fostering adoption through training. These steps contribute to creating an effective and valuable tool in the realm of modern healthcare.
Checklist for Clinical Decision Support System Implementation
Implementing a clinical decision support system (CDSS) in healthcare organizations is a critical task that requires careful planning and execution. Regardless of the technical foundation, the success of CDSS implementation is crucial for healthcare practitioners, and any missteps can have significant consequences. Here is a comprehensive checklist to guide the planning and implementation of a CDSS in a healthcare organization:
1. Building the Team
Assessing Readiness
- Evaluate the organization's readiness to accept and adapt to the new CDSS.
- Ensure a core team is in place that understands CDSS operations and is ready to adapt.
Overcoming Resistance
- Educate healthcare practitioners about the benefits and usability of CDSS.
- Showcase success stories from other organizations that have benefited from CDSS implementation.
Collaborative Approach
- Initiate group conversations involving doctors, physicians, nurses, and IT staff.
- Involve clinical champions, individuals with technical expertise, to facilitate positive discussions.
Addressing Concerns
- Assess internal resources for CDSS implementation.
- Identify and address any resistance from administrative stakeholders.
- Effectively educate the team about the benefits of the new system.
- Ensure stakeholders' concerns are adequately addressed, and feedback is considered.
- Define precise and well-defined roles for team members involved in the implementation.
2. Work with Professional IT Vendors
Recognizing Complexity
- Acknowledge the complexity and sophistication of CDSS technology.
- Understand that off-the-shelf CDSS systems may not meet all unique requirements.
Leveraging IT Expertise
- Work with professional IT companies such as Stfalcon that specialize in healthcare technology.
- Seek vendors with expertise in developing and implementing CDSS.
Customization Needs
- Identify unique functionalities required and assess the need for system customization.
- Ensure the selected IT vendor can provide necessary fine-tuning and customization.
Training Opportunities
- Utilize the engagement with IT vendors to train internal resources.
- Enhance internal expertise in the complexities and technicalities of CDSS development and maintenance.
Successful CDSS implementation requires not only technical expertise but also effective collaboration, stakeholder education, and addressing organizational concerns. By following this checklist, healthcare organizations can navigate the complexities and ensure a smoother integration of CDSS into their existing systems and processes.
Best Practices for Clinical Decision Support System Implementation
A Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS) is a crucial component of healthcare information technology, providing patient-specific data and knowledge to enhance decision-making for patients, clinicians, and staff. Employing best practices in CDSS implementation is essential to ensure optimal functionality and positive outcomes. Here are key best practices:
Calculate the Burden
- Collaborate with software vendors to determine the burden associated with CDSS implementation.
- Assess necessary IT resources to adequately support functionality.
- Evaluate the clinical expertise of software vendors to ensure accurate customization.
Structured System Design
- Design and implement the CDSS with a structured system to streamline data flow.
- Implement governance processes for ongoing oversight and timely error resolution.
Updated Data
- Ensure regular updates of data for effective CDSS functionality.
- Integrate the system with diverse data sources to facilitate accurate and timely data updates.
Clinical Guidelines Integration
- Integrate clinical guidelines and order sets into the CDSS for effective report design without compromising effectiveness.
- Utilize various templates for document creation and provide diagnostic support.
Customization for Workflow Optimization
- Customize CDSS tools to optimize clinical workflows for both patients and healthcare providers.
- Implement reminders and tools tailored to the specific needs of patients and clinicians.
Stakeholder Education
- Educate healthcare practitioners, patients, and staff on the benefits and functionality of the CDSS.
- Facilitate training sessions to ensure effective utilization of the system.
Continuous Monitoring and Evaluation
- Implement continuous monitoring mechanisms to assess CDSS performance.
- Regularly evaluate and update the system to incorporate advancements in healthcare knowledge.
User-Friendly Interface
- Design a user-friendly interface for easy navigation and adoption by healthcare professionals.
- Prioritize simplicity to enhance user engagement and overall effectiveness.
By incorporating these best practices, healthcare organizations can maximize the benefits of CDSS implementation, ensuring improved decision-making, streamlined workflows, and enhanced patient care.
Our Experience
HospApp
Our client envisioned the development of a cutting-edge mobile system fostering seamless communication among healthcare professionals within patient-specific groups. This innovative platform facilitates effective interaction, file-sharing, prescription management, and task execution tailored to individual patients within designated groups. Importantly, all patient information remains highly secure, confined within the hospital's digital walls.
Key Objectives of the System:
- Reduced Patient Waiting Time: Enhance service quality by minimizing patient waiting times.
- Swift Emergency Response: Enable quick and efficient responses to emergencies, thereby mitigating risks for patients.
- Automation for Staff: Streamline documentation, interaction, and management tasks, automating routine processes for the medical staff.
- Secure Information Environment: Ensure the confidentiality and security of patient information, preventing data from leaving the hospital's secure digital ecosystem.
- User-Friendly Interface: Develop an intuitive and user-friendly interface that looks like popular messaging apps, ensuring ease of use for individuals familiar with messaging platforms.
The overarching goal is to transform healthcare delivery by leveraging technology to enhance collaboration, automate processes, and provide a convenient interface for medical professionals, ultimately benefiting both healthcare providers and patients.
IsDocIn
The primary objective of this project was to develop a mobile application to facilitate the appointment scheduling process for individuals seeking medical consultations. The application targeted both patients and doctors, offering a platform for seamless appointment management.
Key Features and Accomplishments:
- User Interface Design: Designed a user-friendly interface tailored for patients, ensuring ease of use and a positive experience.
- iOS and Android Versions: Developed comprehensive designs for both iOS and Android platforms, optimizing the user experience on different devices.
- Native App Development: Implemented the designed UI into fully functional native applications, delivering optimized performance and platform-specific functionalities.
- Doctor Profiles and Notifications: Enabled doctors to set up profiles within the app, providing essential information for patients.
- Implemented a notification system to alert doctors when an appointment has been booked with them.
By successfully creating a mobile application that simplifies the appointment scheduling process, this project aimed to enhance accessibility to healthcare services, offering convenience for both patients and medical practitioners.
Bottom Line
Developing and implementing a clinical decision support system demands specialized expertise in the realm of IT telemedicine services. You require an IT team not only proficient in technology development but also possessing a profound understanding of the financial, regulatory, and administrative intricacies inherent in healthcare tool development. This is crucial to ensure patient safety and safeguard critical information against cyber breaches.
At Stfalcon, we boast the expertise and experience needed to craft robust and entirely tailored telemedicine software for healthcare organizations. Our goal is to elevate internal controls, efficiency, and healthcare services. As a leading medical software development company, we provide the resources essential for the successful development of a fully customized Clinical Decision Support System (CDSS) tailored to your organization's unique needs. Contact us for innovative solutions and a transformative healthcare experience.
 Read the full case study
Read the full case study
 Read the full case study
Read the full case study



