Off-the-shelf patient monitoring systems may seem a convenient solution, but they often do not meet individual hospitals' unique workflows and complex needs. Such approach can result in inefficiencies, restrict scalability, and create integration challenges that ultimately hinder operational efficiency. At the same time, custom remote patient monitoring software provides a strategic advantage for hospitals looking to remain competitive and prepared for the future.
Custom solutions are designed to fit your hospital's workflows and meet your operational goals. They provide the flexibility to handle different numbers of patients and support new technologies. Custom systems work well with your current setup, creating a smooth and efficient system.
This article will walk you through the process of building a customized patient monitoring system designed to meet your hospital's specific needs. You will learn how to identify key requirements and choose the appropriate technology stack.
Stfalcon’s team leverages our 15 years of experience in software development, including healthcare solutions, to show you the process of building patient health monitoring software. Let’s take a look at the key points you should consider at the initial stages of your project.
Core Features of a Custom Remote Patient Monitoring System
As soon as you’ve decided to develop remote patient monitoring software, you should consider the following aspects:
- how patient data will be collected
- how the information should be presented to doctors and care receivers
- in what way a doctor-patient interaction will be realized
- how a software solution will interface with the patients.
Integration with Medical Devices
You can use wearables, accessories, smart sensors, and medical devices to monitor your health. Apps like HealthKit, Google Fit, and other custom applications can help. Heart rate, activity level, body temperature monitoring can be realized in such a way and tracked along with clinical records.
The patients’ data can be shared via specific secure APIs or via a Bluetooth or direct Wi-Fi connection.
Integration with hospitals
Doctors should get real-time patients’ data and hassle-free access to it to provide prompt advice, guidance, or help. Thus, a remote tracking solution should be connected to the hospital’s EHR/EMR system through a secure API. It should adhere to the due healthcare standards adopted in the country in which the HMS operates.
Interaction between a doctor and a patient
Nowadays, video conferencing is a highly welcome feature for such software solutions since you can communicate with and examine patients to some extent. Though for the systems developed from scratch, it may seem a costly feature, it’s better not to cut costs on it.
There are reliable video conferencing SDKs that can operate cross-platform and support end-to-end encryption security to choose from. Besides, these tools support real-time chats, which is vital for effective treatment and care through remote patient monitoring platform.
Notifications
It is important to notify when a patient has a serious condition or symptoms in a health monitoring system. These can be push notifications, SMS messages, or alarm alerts. It's important that they are synchronized for both doctors and patients across their respective platforms. Patients can use a mobile app to monitor their health. Doctors will receive alerts on their pagers, mobile devices, cloud applications, or via email.
It’s essential to consider HIPAA requirements and not include the patients’ data in notifications.
Data Storage and Analytics
When considering rules and regulations, you need to decide which patient data is necessary to keep. Developers must take robust security measures to ensure data safety. It includes data encryption, access control, using HIPAA-compliant storage, and conducting regular security audits.
As long as the data is secure, they can be used for predictive analyses. This is where AI shines, used for detecting health issues at early stages based on patient’s health data.
Want a web app that does more?
Let's build a solution that's smart, sleek, and powerful.
Alina
Client Manager

Remote Patient Monitoring Software Development: Layers, Architecture, Functions
Comprehension of the RPM working principles and the way its layers interact will help you create a remote patient monitoring application that operates like a clock. During the healthcare software development process, you need to remember that any system needs training for both medics and patients. That’s why it’s important to make the interface easy to use for people who aren’t technical.
Further on we deal with HMS Architecture in more detail.
Architecture
The hospitals’ monitoring systems naturally comprise hardware and software components, programming interfaces, data analysis algorithms, and custom features.
Variable microprocessors, low-power amplifiers, ADC converters, LCDs, and sensors belong to the hardware part. The software collects information, stores it in cloud databases, processes it, and displays it in real-time. It can also notify a medic or a family member in case of an emergency.
The functionality of an RPM is distributed between its layers: perception, API, E-health app, or service.
So technically the 4 layers of the system are:
Sensitive Layer
This initial level includes various sensors that collect the patient’s data and send it to processing equipment. You can program your tool so that a medic can track patient’s sugar level, blood pressure, or heartbeat. Besides, the person’s location can also be set to track (a helpful feature for patients with memory disorders supervision).
API layer
Various APIs are used at this layer to store information about new patients and display data about those registered in the system. This layer, the central part of any RPM system, is enabled when the patient's information should be fast-forwarded to the doctor.
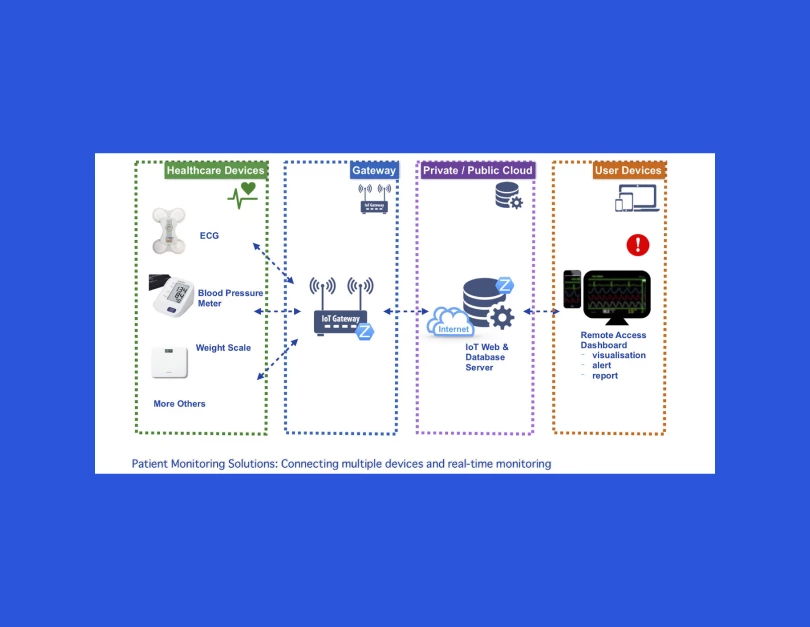
Data processing
AI helps analyze information to check the health of a sick person. If there is an emergency, the system will alert the doctor. Moreover, AI can detect a threat, even when everything looks normal to the doctor and the care recipient.
Application
The doctor gets a notification into the app installed on a mobile device or PC as soon as the information is processed. After checking all the details, a medic can decide what to do next. They can choose the immediate steps or plan for further treatment. More than that, a good HMS can analyze the information received from wearables and make AI-based suggestions for the potential diagnosis and course of action to stabilize the patient’s condition. An AI program looks at data and compares it with information from other patients. It then creates a prescription or suggests a solution.
How to Build a Remote Patient Monitoring Software
Here, we will describe the software development process as it happens at Stfalcon. Our team uses the Agile system, where we design, develop, and test each functional block at the same time. This lets us be flexible, adapt to changing requirements, and demonstrate consistent progress to our clients.
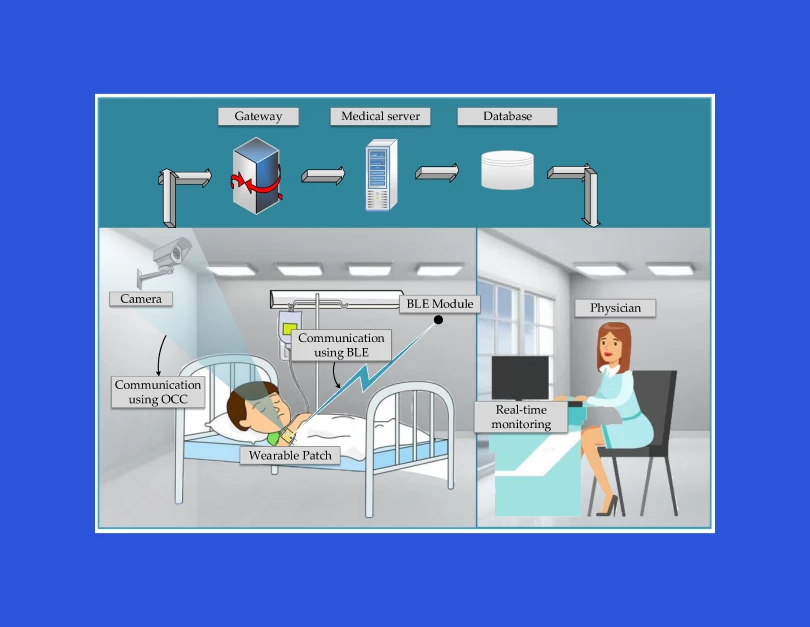
Discovery and Requirement Gathering
At this stage, we analyze our client’s requirements, current market trends, and target audience. Then, together with our client, we define the project scope and decide what features we need to prioritize. As a result, our client receives a detailed work plan and cost estimation.
Choose the Right Technology Stack
This is a crucial step to ensure scalability, reliability, and seamless IoT integration. For the backend, frameworks like Node.js or Python are popular due to their versatility, performance, and strong ecosystems. These technologies support real-time data processing and can easily handle the demands of RPM systems. When connecting IoT devices, you can use different communication methods based on the devices and what you need. Options include MQTT for quick and simple communication, Bluetooth, and Wi-Fi. For data storage, cloud solutions such as AWS, Google Cloud, or Azure provide scalability and ease of access, making them ideal for most RPM projects. On-premise databases like PostgreSQL or MongoDB may be preferred for organizations with strict data control or compliance needs. Balancing these technologies based on project goals ensures a robust and future-proof solution.
Develop and Test Core Modules
Designers create a user-friendly interface, while developers build the front-end and back-end systems. At this point, decide which features are most important for your Minimum Viable Product. Focus on things like sharing patient data, connecting with electronic health records (EHR), and setting up alerts and notifications. After we build each functional block, we carefully test the application to find and fix any issues. This encompasses functional testing along with usability, performance, and security assessments. Every other week, the team completes a functional version of the application. While it might not be suitable for end users yet, this shows the advancement of the project development. This approach helps us stay ready for changes in requirements. It also prevents us from having to redo work that has already been approved.
Deployment and Training
When launching the MVP, it’s important to address all significant bugs and incorporate all essential features. However, even after resolving the major bugs that affect the app’s functionality, the client should understand that live interaction with real users will uncover minor bugs that need fixing. This is a typical part of the process.
Healthcare professionals need training on the new solution and its features. This training will help them achieve the expected business benefits.
Maintenance and Updates
Stfalcon provides support for the launched product and keeps enhancing the software solution and optimizing it. This support includes development and maintenance, bug fixes, testing infrastructure, monitoring, and applying updates.
After launching and testing the MVP, we will analyze its performance and gather user feedback. This information will help us improve and develop the next version of the product.
Challenges in Developing a Custom Remote Patient Monitoring Software
Integration with Existing Systems
The first challenging task is ensuring seamless connectivity with legacy systems. Remote patient monitoring solutions need to access and process a lot of data. However, many hospitals still use old software that does not easily work with newer technologies.
Solution: Developers need to think about data formats, interoperability standards, and API integrations. This helps ensure smooth data exchange and analysis within the application. Transit to newer solutions may require data migration to transfer important data from legacy systems to a new database.
Data Privacy and Security
We have already emphasized the importance of data protection in healthcare software. These solutions must follow local laws, such as HIPAA in the United States.
Solution: To ensure data protection, security must remain a priority at every stage of development. Developers need to implement security measures like multi-factor authentication and data encryption. A complete risk assessment plan is necessary to identify and mitigate potential security threats. It is vital to select a HIPAA-compliant backend service provider and to separate Protected Health Information (PHI) from other data within the app. Your app needs to have a clear and simple privacy policy. This policy should explain how you will collect, use, and protect personal health information (PHI).
Cost and Timeline Management
Balancing the need for a highly customized solution with budget constraints can be challenging. Customizing software to fit specific workflows, integrating various IoT devices, and ensuring compliance with healthcare regulations often results in increased development time and costs. Delays or changes in the project can increase costs, making it harder for stakeholders to find the project worthwhile.
Solution: Embrace an agile development methodology that emphasizes iterative progress and flexibility. By dividing the project into smaller, manageable phases, stakeholders can focus on delivering core functionalities first and gradually incorporate advanced features. This method helps manage budgets better, speeds up product launches, and allows for early feedback. This way, the final product meets business goals and financial needs.
User Adoption
Healthcare professionals often have busy schedules and face challenges when learning new technologies. If a system is complicated or hard to use, it can lead to resistance and underuse. This creates inefficient workflows and reduces the overall effectiveness of the solution.
Solution: Make interfaces easy to use with few navigation steps. Include features like dashboards for specific roles and alerts that provide real-time updates. Providing comprehensive training and ongoing support further ensures that healthcare professionals can quickly adopt and effectively use the system in their day-to-day operations.
One of the easiest and most cost-effective solutions for any of these challenges is to partner with an experienced healthcare software development company. An expert team can help you develop custom monitoring software that will address your business needs without a hassle and excessive budget.
Stfalcon Experience
The Stfalcon team is not new to healthcare software development. And though we don’t have RPM systems in our portfolio yet, some of our other cases from the industry can give you an idea of what we’re capable of.
STRONGMom
STRONGMom is a fitness app that can be used before, after, and during pregnancy. Users can create a personalized training system based on their physical condition. They can track important factors, like weight, and record their progress.
The team decided to register users by their status (before, during, or after pregnancy). The business logic was divided into three main functionalities: activities, calendar, and timeline.
The core business logic is implemented in the backend, which provides a REST API for data exchange with mobile client applications. The admin panel, used for adding exercises, creating programs, and managing the system, is built with Symfony and utilizes EasyAdminBundle. This allows for convenient customization to meet the specific needs of the project.
Online doctor appointment booking system
The project aimed to create an online booking system for scheduling appointments with doctors at the medical center, along with designing a landing page for this system. Additionally, the solution should enable new patients to register and select a doctor.
The services offered by Stfalcon encompass full-cycle product development, including business analysis, user flows, user experience (UX) and user interface (UI) design, front-end development, back-end development, manual testing, quality assurance, and implementation.
We have implemented a fast and easy authorization process within the application. The backend handles REST API queries from the frontend of the app. The app's native data is stored in a PostgreSQL database management system. Data exchange is facilitated with client databases. Additionally, the backend integrates with several third-party services.
Conclusion
With rapid technological progress and growing concern for individual health, remote patient monitoring solutions become one of the most promising niches on the market. Stfalcon team always looks for the best and most cost-efficient ways to implement the functionality that the client wants.
As we already have healthcare software development expertise, we’ll gladly take up the development of a healthcare monitoring system. If you have ideas on how to start, let’s discuss your project together.
FAQ
What is the cost of remote patient monitoring software development?
The cost of development is influenced by the project's scale, complexity, and the technologies utilized. At Stfalcon, the starting price for RPM development is $150,000. We begin each project with a discovery phase, during which we offer design solutions tailored to our clients' needs. Our services encompass both back-end and front-end development, along with thorough testing of the software we deliver. This process ensures that our software solutions function correctly, adhere to all client guidelines and requirements, and provide a convenient and intuitive experience for target users. This comprehensive approach enables us to deliver high-quality results to our customers.
What are the best health monitoring systems on the market?
Some of the best remote patient monitoring systems on the market, as of the end of 2024, are CareVive (focused on cancer patients), Accuhealth (known for its user-friendly interface and wide range of supported devices), BioTelemetry (specializing in cardiac monitoring), and ResMed (a global leader in respiratory care). These solutions are great examples of intuitive design, flawless user experience, smooth integration with healthcare systems, and the ability to accommodate future growth and technological advancements.
Is patient health monitoring profitable?
Short answer: yes. Patient health monitoring systems are profitable due to market expansion, revenue generation, improved customer experience, accuracy, personalized care, and greater efficiency. However, it's important to note that the profitability of PHM depends on various factors, including specific PHM services offered, the target market and patient population, the pricing strategy, operational efficiency, and the ability to manage costs effectively.
 Read the full case study
Read the full case study
 Read the full case study
Read the full case study



