In case you go crazy like most people, when you need to deal with your budget and can hardly say how much you earn and spend, not speaking of investing, timely bill payments, and loan coverage, you need an app for finance management. And you are not alone!
Seven out of ten smartphone users are moving towards using financial apps that keep their data secure and offer customized services tailored to their individual needs. That’s why money management app development is one of the most significant contemporary trends.
Such applications grow in popularity day by day. So we’ve decided to deal with the current trends, technologies, features, and tendencies in personal finance software development to keep our readers up-to-date. In this article, we are going to find out how to build a unique finance app like Mint.
What is the Mint App?
Founded in 2006, as a personal budget tracking and planning app, Mint firmly keeps the leadership among the personal finance management solutions. The application offers its users a variety of easy-to-use financial planning and tracking tools that facilitate budgeting process automation and money saving.
The application offers budget goals setting based on spending so that a user can later adjust or increase these goals. More than that, the Mint app allows credit cards, bank accounts, and other financial accounts synchronization, income tracking, automatic expense updates and categorization, saving goals setting, and much more.
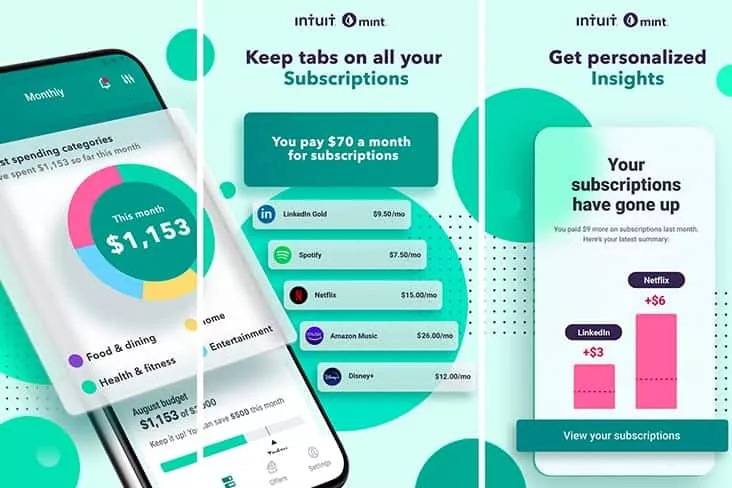
That’s why Mint users appreciate the opportunity to get a clear and comprehensive picture of their financial situation all in one place, along with robust security. So, if you nurture the idea to create a money management app like Mint, you should start your journey by considering the up-to-date market requirements to modern personal finance software solutions. Let’s get down to them and discover what it takes to develop a budgeting app.
Want a web app that does more?
Let's build a solution that's smart, sleek, and powerful.
Alina
Client Manager

Money Management Apps Market Requirements
The market of financial apps is abundant. That's why those who want to develop services similar to Mint, should be ready to face and keep up with the competition in it. There there are not only Big Tech companies, like Apple or Google there but also a variety of small emerging startups. That’s why competitor analysis is a must.
Continuous Competitors Analysis
Obviously, to stand the competition, you need to create a financial tool that provides the users with real value. To do it, look and learn from products similar to yours, especially if you aim to design applications similar to Mint. Though every developer performs competitor analysis slightly differently, the overall picture is always the same.
You need to find your competitors and create a budgeting app better than they offer. On the way, you’ll also ensure that your idea is viable and worth time and money investments, simultaneously learning from other people's failures.
So, you should find your competitors through Google, ProductHunt, Reddit’s r/Entrepreneur, or Reddit’s r/startups sections. Check the major aspects of their business: website, core value proposition, app store rating, and reviews, also look through the social media and find out the way of monetization they use.
On doing all these, you’ll get aware of your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses as well as specifics, so you can then insert your product into the picture.
Later on, long-term monitoring should become your routine task to beat your rivals to the punch on updates, innovative features, and many more factors that you’ll never know about if you don’t watch them out.

Chatbot Implementation
The usage of virtual assistants is a modern trend gaining momentum in the financial sphere. Chatbot integration is essential for any application or platform. A budgeting app like Mint can help track expenses and prompt how to save money more effectively. In such a way, you can simultaneously reduce the workload of the support team and streamline the user experience.
Cryptocurrencies Including
Digital currencies and crypto assets nowadays take their place alongside fiat means and stocks. So, to meet the needs of your audience, you should consider this. The Mint app, for instance, allows bitcoin balance management, while some other solutions already allow cryptocurrency trading and digital wallets management. To ensure your software competitiveness, integrate AI chatbot into it.
UI/UX High Performance
Personal finance application is something very private and rather sensitive with complex functionality. To create a finance app like Mint and make it convenient for the users it’s very important not to make it over-complicated, but intuitive and convenient.
Thus, we advise creating UI/UX with all the users' pain points and needs to be considered.
You need to walk your users’ shoes for the purpose and think the way they think. It’s reasonable to provide your audience with a short and fun learning curve, some kind of onboarding tips, and remember about the golden "three taps" rule. Any problem should be possible to be solved in 3 taps or even less.
Opt for the simple interface, straightforward navigation, and inclusivity. Try to find the right balance in your UI/UX of including the maximum necessary features on the dashboard and not overloading it.
However, remember, that the trends change for UI/UX and you should keep your app design up-to-date to go with the times, especially if you design applications similar to Mint. Let’s now deal with the features that your app for finances should have at the present time include.
Finance Management Apps Must Have Features
The state-of-the-art finance manager app helps users track their income and expenses. Yet not only, but it should also facilitate budget optimization and effective personal capital and wealth management along with financial literacy. Thus, if you want to develop an app similar to Mint and to meet the demands of the modern market, it should possess rich functionality.
Account Creating
This feature goes without saying that the users have to register and enter their personal data and financial details for their finance tracking. Authorization and security are something to pay special attention to. Financial data is extremely sensitive data, consider two-factor authentication, face recognition, voice recognition, fingerprint, unique code generation, or some other measure to protect your users' data.
Account Access
The user account access should be secure since it deals with personal and financial data. However, you need to connect your user account in the app with cards and bank accounts, that’s why guarded passcode is a must. The login/logout procedure should be taken every time a user interacts with the application. It’s smart to allow short-term sessions (sessions with a limited lifetime) it will minimize the chances for the app to run unprotected.

Data Security
As we’ve mentioned and not once, data security is the number one concern for money management tools development. You should not only create a solution and provide secure authorization, but also ensure data security at every level of the data channel. Consider the encryption and storage of the transmitted data at a minimum with a standard SSL protocol.
Avoid open-source libraries but also closed-source cryptographic libraries, since they don’t allow checking their trustworthiness and proficiency. Go with the tides and check the sophisticated methods to enhance your app security when they appear, test them and apply them if the game is worth the candle.
Bill Reminding
Introduce the functionality of bill tracking, it will allow your users to keep and monitor all their bills in one place. But it’s even more preferable to implement the feature of notification as to what and when a user should pay so that no payment is missed.
Notifications
As we have mentioned above, notifications are reasonable not to miss payments. However, it can also be utilized for keeping users aware of their low balances, goal milestones, late fees, suspicious operations, and much more.
The Data Synchronization
Budgeting app should be able to synchronize all the user accounts, as well as credit and debit cards. Thus, a person will get a comprehensive overview of all the transactions, bills, fees, operations, loans, investments, and whatever else for effective budget management.
Investment Recommendations
Along with investment tracking, help your audience stay on top of market benchmarks. Introduce AI analysis and prompt them with the best options for asset allocation such as brokerage accounts, mutual funds, IRA or real estate investments, etc.
Entertainment Element
A bit of entertainment adds up lightness and simplicity to serious financial matters. So entertaining features are essential. Mint introduced gamification to encourage user engagement with the app. You can also consider some reward systems, setting goals and marking achievements through a certain point system, for instance.
Fast Access to Transactions
You can not only provide your users with the transaction details all in one place but also categorize the spending transactions for the users to effectively track their expenses.
In Mint, it’s possible to select all the specific transactions from a certain merchant or category and set a category for them. The app also allows hiding transactions. You can consider your own pattern according to the needs of your target audience.
Profile Operations Analysis and App Behavior Adapting
Using the feature of analysis, users can track their financial activities, manage and save their means properly and adjust spending accordingly.
A good idea is to allow daily weekly monthly and annual reports for incomes and outflows, categorized, summarized, and possibly with estimates, advice, or predictions for the coming period.
The users will appreciate a budgeting option to plan their spendings for a week, a month, or several months. Allow setting spending limits, and notifications to avoid overspending in your newly-developed financial app.
Through a careful user behavior analysis based on app data, user behavior patterns and variations can be discovered for further budget enhancements.
We can speak a lot about the app features, but let’s touch upon the tech aspect and platforms to implement all these features.
Mobile Finance App Development Platforms and Tech Stacks
As you can understand from the above, native development relies on programming languages, tech stacks, and tools designed for one platform. The developers in such cases are guided by specific requirements of a chosen platform, while cross-platform development allows the creation a single app for several platforms.
The Stfalcon team is experts in any kind of development, so the lists of tech stacks for different kinds of apps like Mint, can be found below.
iOS Technology Stack For Personal Finance App Development

Android Technology Stack to Build Fintech App Like Mint
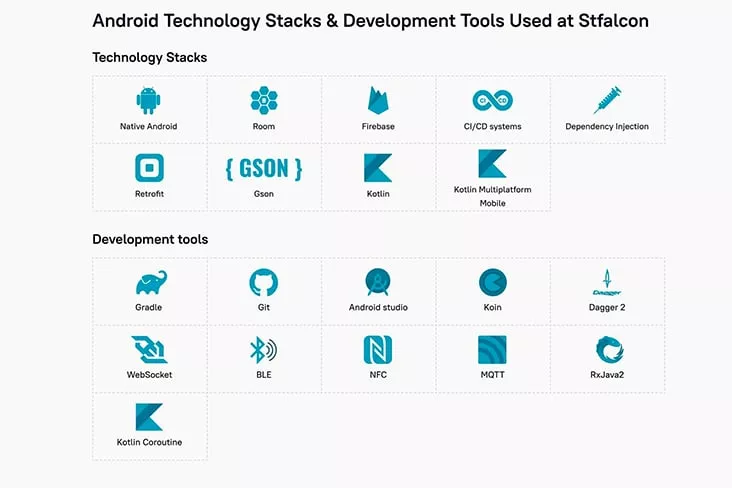
As soon as you have a list of features for your money budget app, you should make up your mind on the type of it, and consequently instruments and technologies to use for development. If you feel bewildered with all these terms, like frameworks, programming languages, libraries, etc., just contact the Stfalcon expert for a comprehensive consultation.
Meanwhile, let’s take a closer look at the process of development.
Fintech App Development Process
To craft the best money management solution and outperform your competitors, you should approach the lengthy and complicated process of development with full seriousness and responsibility. The first step to a fully-functioning solution is requirements gathering.
Requirements
This stage is traditionally called the discovery stage at Stfalcon. It comprises user research, competitor research, and tech and business research. Our specialists try to find out as much as possible about the market, target users, competitors, and their products, trends, risks, and opportunities.
So, during the discovery stage, we get a profound understanding of the market, the app’s target audience, its pains, and requirements. We make assumptions, validate ideas, and as a result form a unique value proposition, that can help stand out among the competitors and existing products. The initial phase of designing an application similar to Mint involves our vision and project estimation to our client for agreement.
Development
As soon as all the details are agreed upon, the process of development takes place. To create the best budget manager app, you should implement the best UI/UX design. It’s vital to make a product functional, yet intuitive and user-friendly, so then the solution will appeal to your audience. Frontend/backend coding is realized according to the app type and specifics.
Software Testing
Software testing is one of the most important steps in the development process before the new solution is released. You have to make sure that the app operates and behaves as expected and desired.
It should run smoothly and error-free.
Testing can be manual and automated, realized on different levels. The details, requirements, and KPIs are discussed with the client at the very beginning of the project. So, at this stage, we ensure we have provided the proper product quality to our clients and app users.
Publishing App
Nobody will know you have the best budget manager app before you publish and market it. We help our clients with publishing apps on Google Play and App Store, purchase accounts for the app publication, and conduct releases.
Support & Maintenance
After the app is built and released, Stfalcon in most cases continues to maintain its infrastructure. We troubleshoot if there are any bugs reported by the client, and handle the problems that may set in.
The scope of maintenance and support is determined and regulated by the contract, as a rule.
Here, we will address some common concerns and provide insights to guide you a bit in creating a finance app that helps users better manage their money.
FAQ About Personal Finance Apps
What do customers expect from personal finance apps?
Customers expect finance apps to help them track spending, set budgets, and reach savings goals. One of the most important aspects is security. Users want to know that their financial data is safe and secure. Developers need to focus on security measures to protect users' sensitive information. These measures are encryption, secure servers, and strong authentication. The budgeting app development team should also focus on creating a simple, intuitive user experience.
What Features The Personal Finance App Must Have?
When you build a financial app, some key features to have are expense tracking, budgeting tools, and bill reminders. The ability to link multiple bank accounts and credit cards is a must. These features allow users to get a clear picture of their finances and make informed decisions. Other valuable features for personal finance management app development are savings goal setting and personalized financial advice. By incorporating these features, you can develop a money manager and financial tracking app that assists users in managing their finances.
How Apps Like Mint Make Money?
There are a few common monetization approaches to generate revenue for personal finance apps. In some apps, premium features are available for a fee. Other apps partner with financial institutions and earn referral fees. Some offer targeted financial products to users. It's important to have a clear monetization strategy when creating a finance app.
Conclusion
Having extensive expertise in software development, Stfalcon has all the necessary skills, tech stack, and knowledge to develop a state-of-art product for any industry. However, Fintech is the most attractive and the most promising area to enter.
So, let’s discuss your project together and bring it to life.
About the Author
Andrii is an Android developer with more than 6 years of experience in building, integrating, and maintaining Android apps. He has a strong background in the development of enterprise-level software and applications. As a writer, he wrote numerous articles on app development. Currently, he is working with the Stfalcon team.



