Dropbox launched with a simple explainer video. Airbnb started by renting out an air mattress. These weren’t lucky shots — they were smart MVPs. Meanwhile, hundreds of startups quietly burn through budgets building full-scale apps no one ends up using.
The difference? Validation.
At Stfalcon, we’ve helped dozens of startups move from raw ideas to working MVPs that attract users, gather feedback, and evolve into scalable products. MVPs are how you learn fast, build smart, and avoid the trap of pouring resources into assumptions.
This article is your guide to getting it right: why MVP solutions for startups matter more than ever, how we help startups design and develop them strategically, and what real success looks like when you launch lean.
Why Do Startups Need MVP Development?
Startups don’t fail because they can't build a product—they fail because they build the wrong one. In early-stage ventures, time and capital are limited, but assumptions are plenty. That’s where MVP development for startups comes in: it’s not just about building faster, but building smarter. Based on our work with early-stage startups, here’s why investing in an MVP is a strategic necessity, not a shortcut.
De-risking Your Vision: Fail Fast, Learn Faster
An MVP is your first real experiment. It’s how you test core business and user assumptions without committing your full budget or timeline. Most startup failures still come down to one issue: no market need. Our software product discovery services help identify and prioritize the most important assumptions. This way, you can avoid spending time and resources on features that no one wants. With an MVP, failure isn’t fatal—it’s informative.
Capital Efficiency: Maximizing Every Dollar
Startup budgets are tight, and every dollar must work hard. Building a complete product without checking if people want it is a common mistake. This often results in wasting resources on features that nobody needs. An MVP for startups allows for optimizing a limited budget by focusing only on what's essential to solve a core user problem. Our lean development methodologies, including Agile sprints and focused iterations, ensure efficient resource allocation, preventing overspending and maximizing the impact of your investment.
Accelerated Market Entry: Seizing Opportunity Now
Speed matters—especially when your competitors are racing to solve the same problem. Startup MVP development helps you get to market quickly, start learning from real users, and iterate fast based on what actually works. We specialize in rapid prototyping and short delivery cycles to help startups launch sooner, validate faster, and adjust without delay.
Magnet for Investment: Show, Don't Just Tell
While a compelling pitch deck can open doors, a functional MVP unlocks serious investment. It turns your idea into a real product that demonstrates evidence of interest, user involvement, and a proven market need. Investors are looking for more than just potential; they want proof. We create our MVPs to test ideas while ensuring they can scale in the future. This approach makes them more appealing for later funding opportunities.
Want a web app that does more?
Let's build a solution that's smart, sleek, and powerful.
Alina
Client Manager

Companies that Started as MVP Products
Spotify
Spotify MVP developers stuck to the primary function: online music streaming. After learning the results of the closed Windows app beta testing, developers managed to secure deals with major record labels and secure substantial investments for their startup project. Today with 60 million current users Spotify is worth $8.4 billion.
Spotify today
Foursquare
Foursquare MVP product had only one feature: check-ins and badges for them. After studying user reaction MVP developers started expanding it and added recommendations and city guides. Today service brings together 50 million people that checked in 8 billion times.
Foursquare MVP
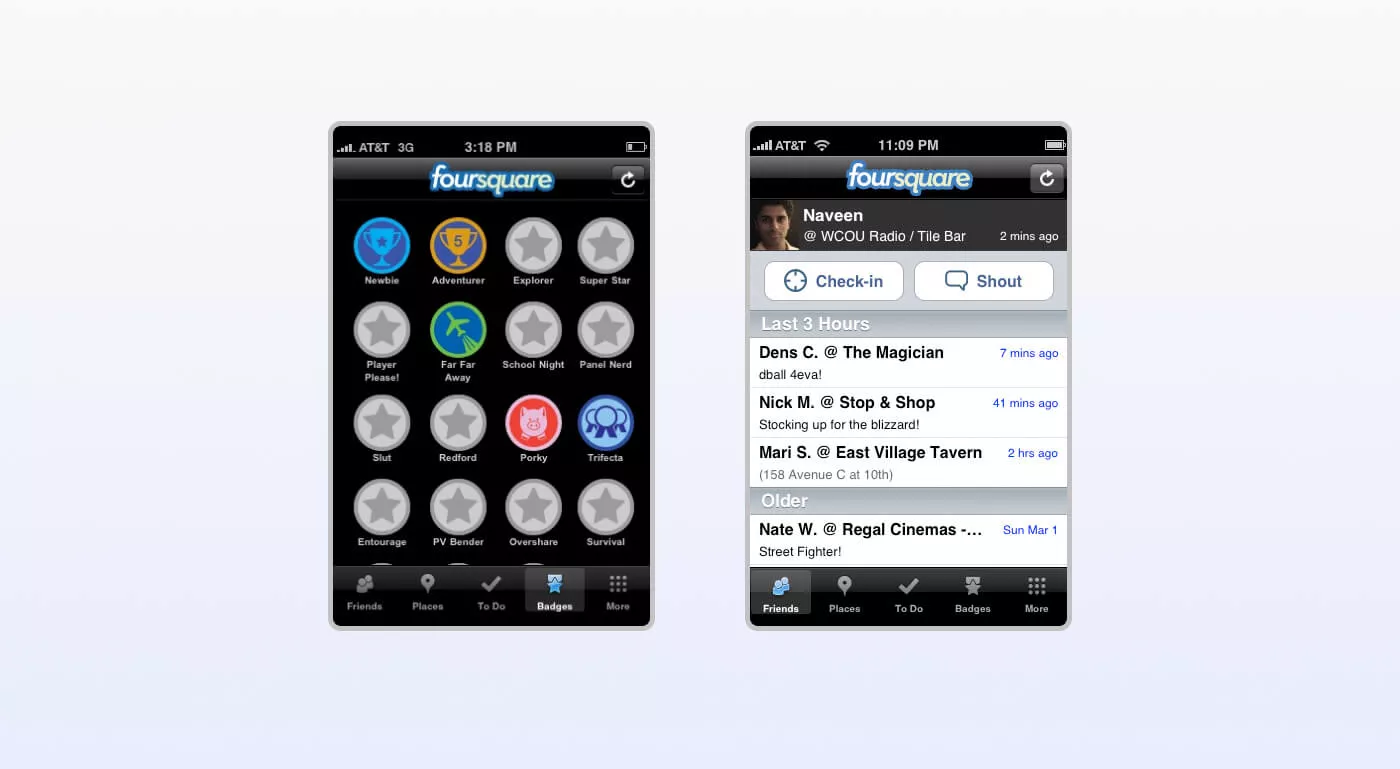
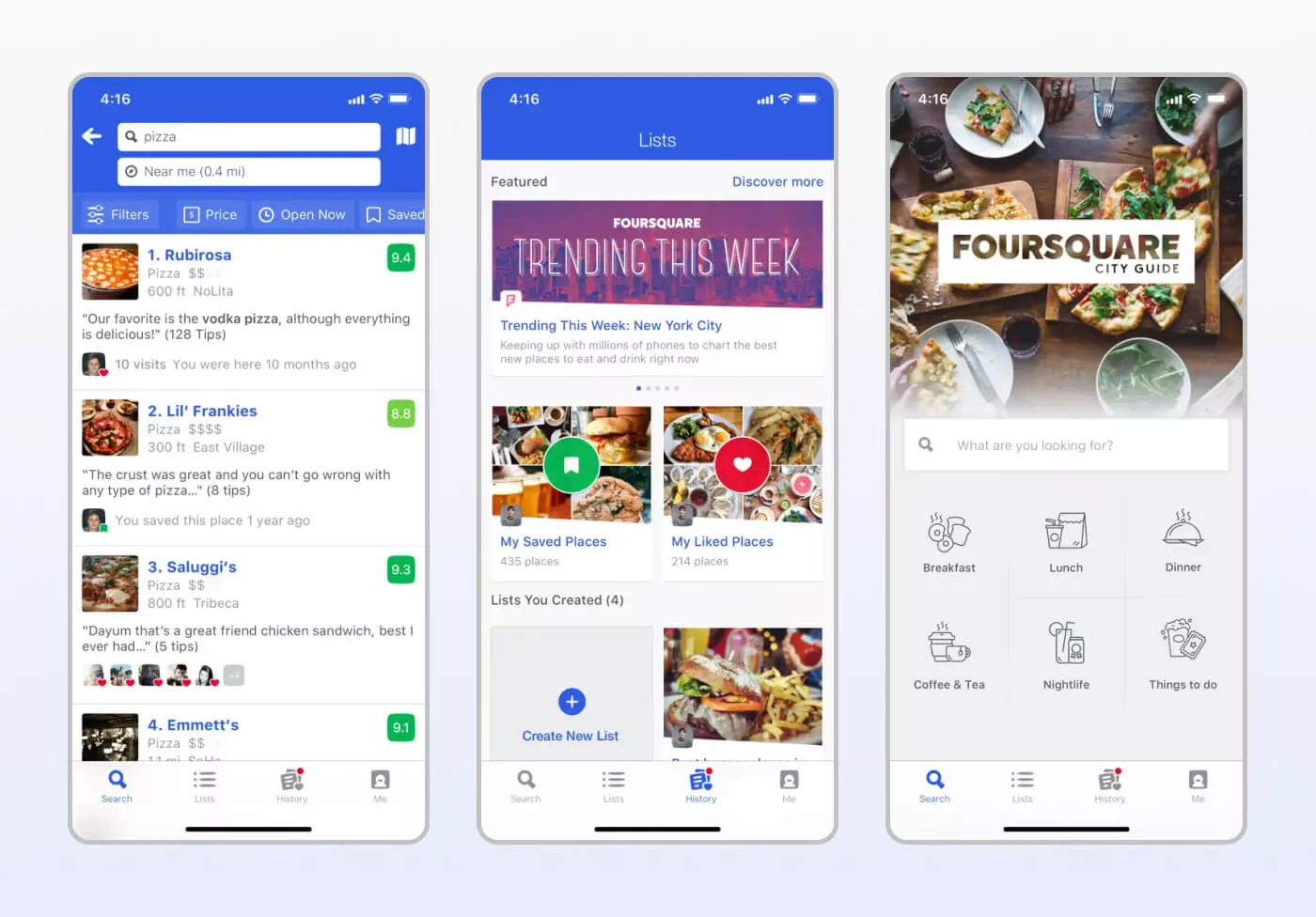
Foursquare today
Airbnb
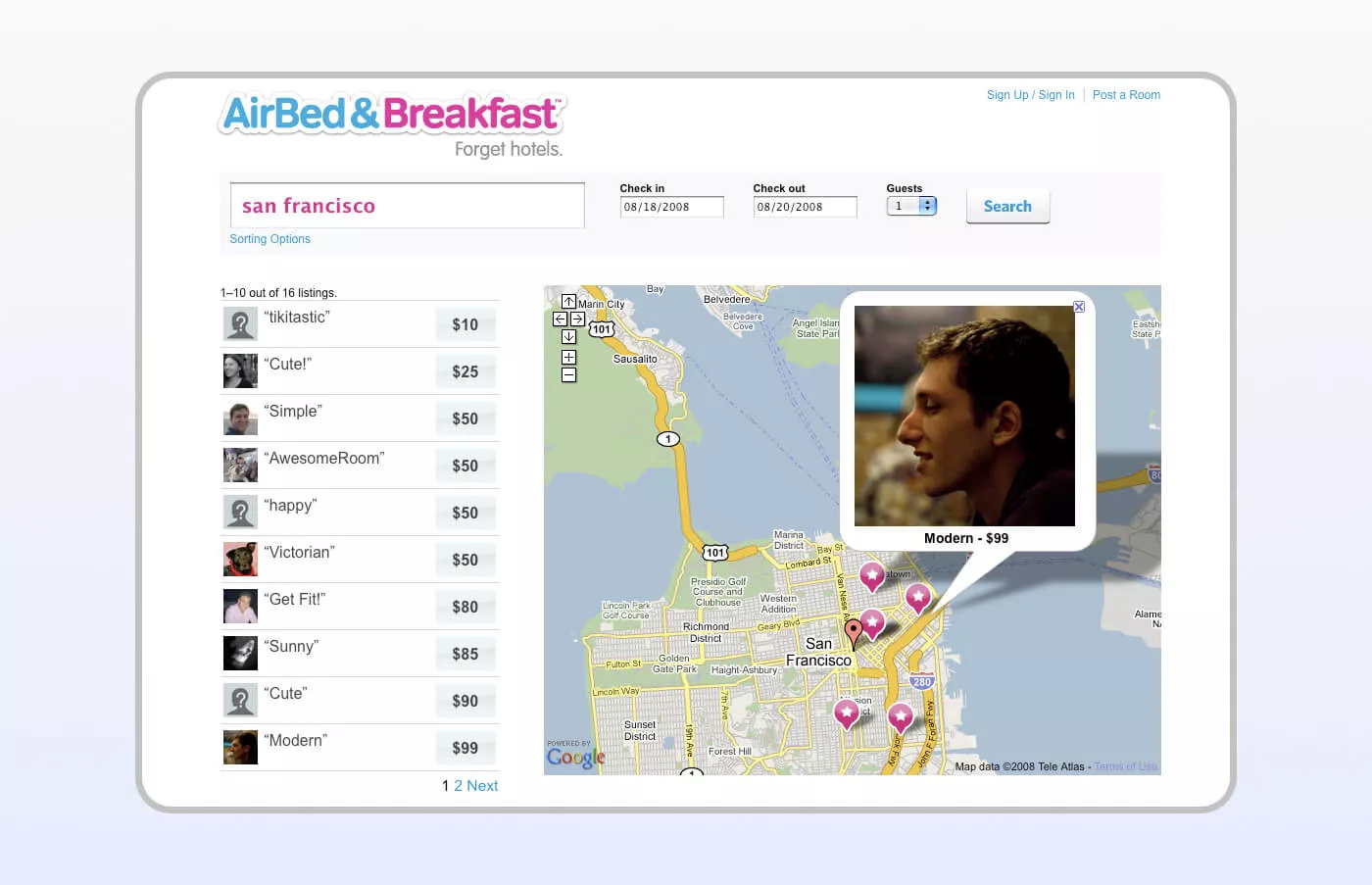
The service offering short-term rentals to travelers began with its owners renting their apartment to a few participants of the San Francisco design conference. They made photos of the place to create an Airbnb MVP in the form of a simple website, and soon were welcoming the guests. This way, startup owners could check whether their idea of a short-term rental would appeal to users.
Airbnb MVP
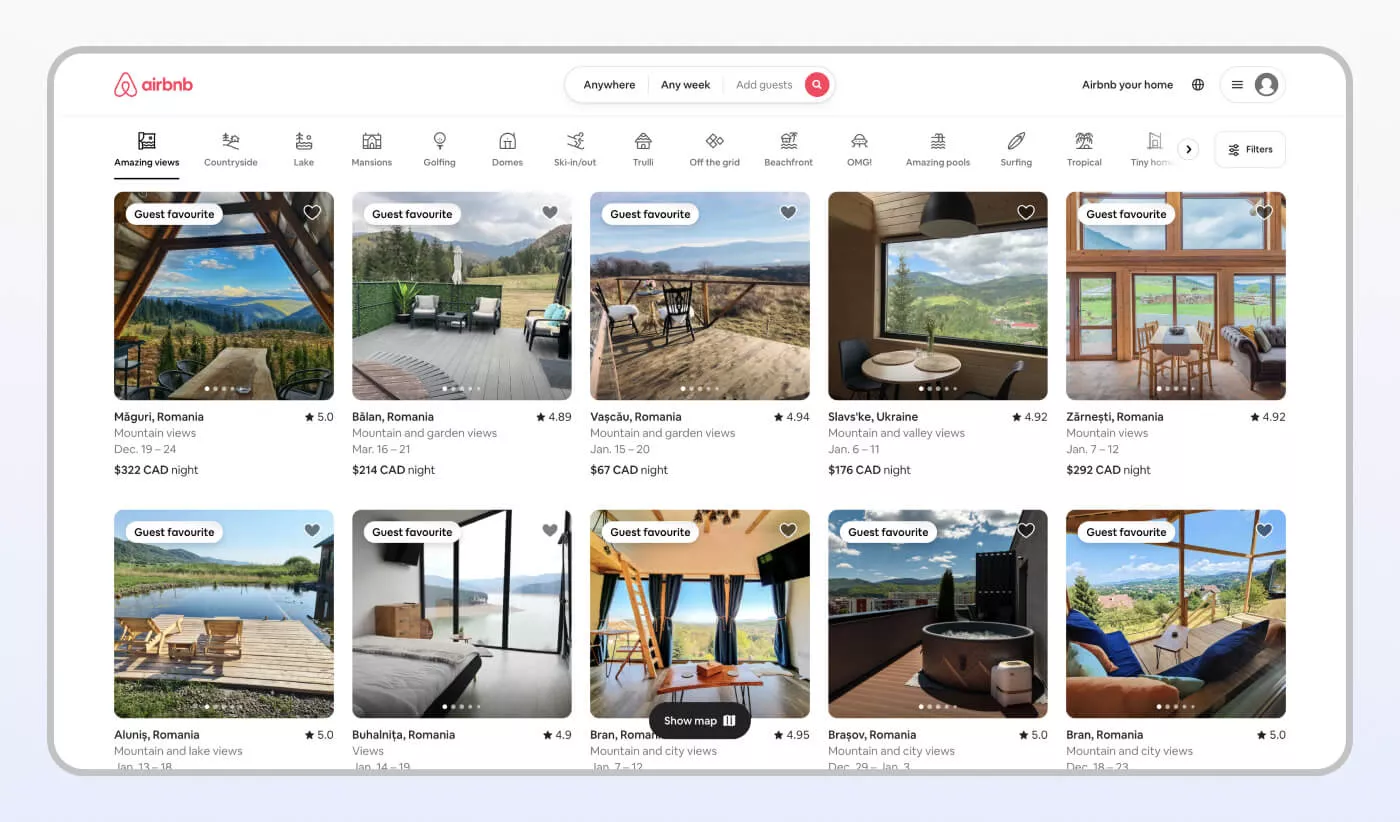
Airbnb today
Groupon
Before testing their hypothesis about group discounts, the Groupon creators started a website called The Point. It was aimed at finding like-minded people to accomplish a goal that could not be reached otherwise. But the idea needed to be more focused. So, the Groupon founders created a customized WordPress blog to post information on group discounts manually. After users signed up for a particular discount, a PDF file was sent to their email address. This way, the Groupon founders managed to test their MVP hypothesis (that users like the idea of getting a good bargain) with minimal effort and investment.
The Point, first Groupon MVP
Groupon today
MeinFernbus
Today, MeinFernbus is a leading company in the German long-distance bus transportation market. In 2015, MeinFernbus merged with another company, which increased its market share to 76%.
MVP development for startup we did together with the MeinFernbus IT team was quite simple:
- Users open the website
- Choose route and date
- Buy tickets
- Print them out
- Shows the ticket when boarding the bus.
MVP allowed to buy tickets only for several buses going between Freiburg and Munich. Some of the operations were manual, and users could only pay with euros.
When MVP was successfully checked on practice, we started expanding it:
- It became possible to reserve places for bicycles, use vouchers, return tickets and make changes to them.
- The number of routes increased, and the project architecture was rewritten to work with higher loads.
- A separate portal for partners and agencies was created, and we developed apps for Android and iOS.
When buses started going to Switzerland, support for the Swiss franc and new payment options were added. A complex system of financial reporting was created. Nowadays, the company continues to use a procedure for buying tickets that was tested with an MVP, but underneath it lies a very different and complex system.
MeinFernbus MVP
MeinFernbus today
BingeBooks
BingeBooks is an online community created by authors and book lovers. For an MVP, we have built a mobile app for iOS and Android, focused on the main functionality - content search, book browsing and managing user lists.
As a part of our startup MVP development services, we focused on the essential functions that allowed users to discover, explore, and organize books effectively, proving the concept's viability. The initial product provided recommendation lists from the service's authors, a clear search function for books and authors, and comprehensive book information views (description, average ratings, user comments, and purchase options).
According to the research studying 3,200 fast-growing mobile and internet startups, in 74% of cases, the reason for startup failure is premature scaling. The company's revenue from new users turns out to be lower than the expenses incurred by providing services to them. This problem arises from a lack of knowledge about the target audience's needs and preferences. However, you can avoid it: partner with a startup MVP development company and adjust your initial startup hypotheses based on the actual data gathered through the MVP.
How to Build an MVP for a Startup: Stfalcon’s Approach
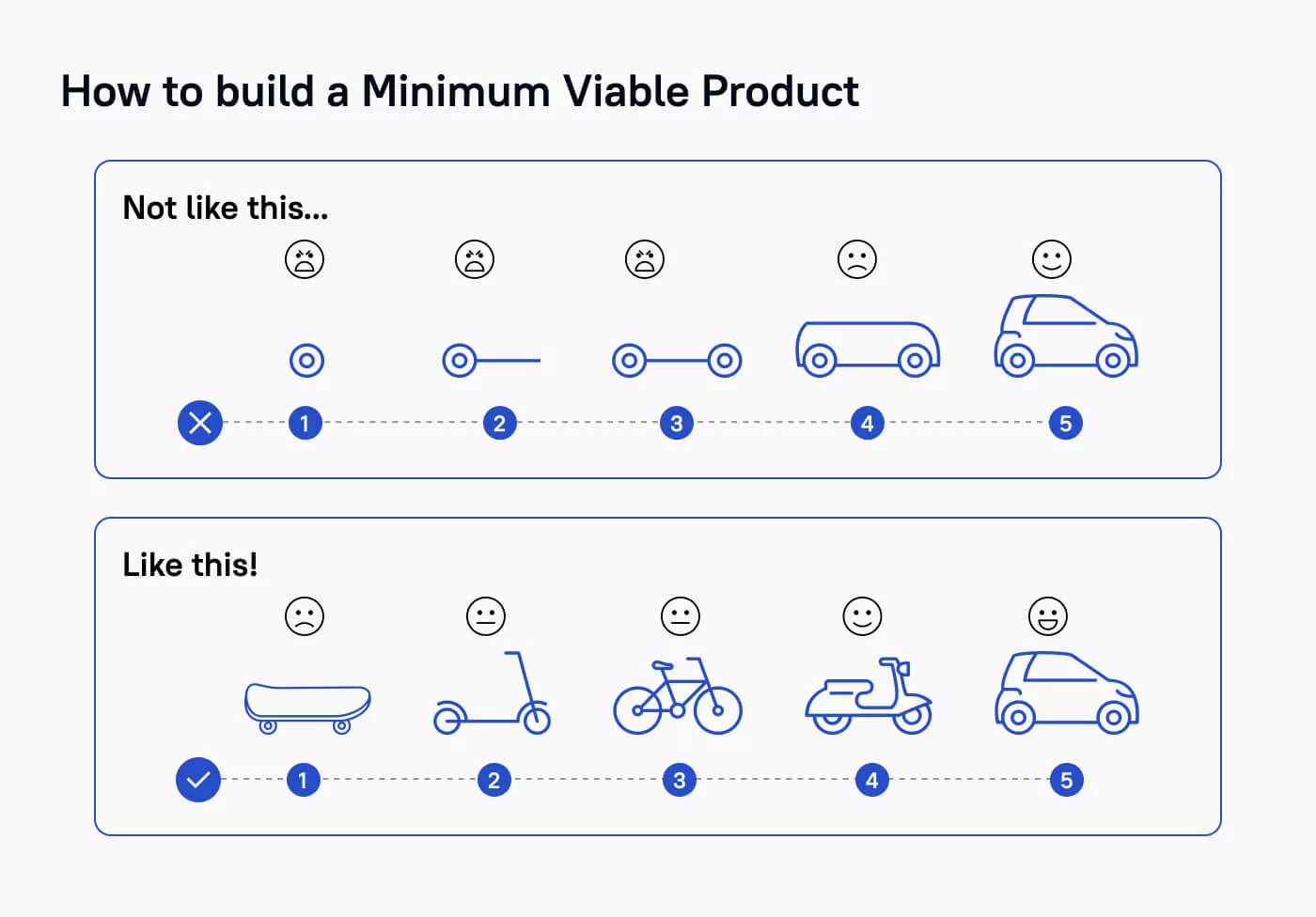
It's one thing to know why an MVP is crucial; it's another to execute it flawlessly. At Stfalcon, our approach is rooted in proven methodologies and a deep understanding of startup dynamics. We don’t just build what clients ask for — we help them uncover what their users actually need. Our MVP development services for startups are designed to validate ideas early, prioritize smartly, and deliver functional products that can grow. Here’s how we do it.
Step 1: Strategic Discovery & Problem Validation
A truly successful MVP app development for startups starts beyond simple requirements gathering. Your initial ideas do matter, but our unique process takes it a step further to determine what the actual issue your client's users are actually addressing.
We begin MVP building for startups by diving into your vision, often employing tools like the Lean Canvas to solidly define your business model, customer segments, unique value propositions, and key metrics. This template includes tools to help you get to know your target users deeply. Utilize the user journey mapping method to identify their problems and goals. Utilize competitive analysis to identify gaps and opportunities in the marketplace. Additionally, utilize stakeholder interviews to hear key opinions. Together, these methods give you a clear snapshot.
This careful phase helps us focus on the main value we provide. It aligns the MVP with key business goals, ensuring we build the right product from the start.
Step 2: Ruthless Prioritization & Core Feature Definition
The hardest part of startups MVP development isn’t coding—it’s deciding what not to build. We work closely with you to strip your vision down to its most essential, high-impact elements.
We prioritize features around the core user problem, always aiming for early validation over completeness. Real users are involved early to guide the decisions during the design process. We avoid over-engineering, instead using flexible and scalable technology that allows for future pivots. Our goal: a focused product that delivers value fast—and can evolve based on what users do, not what they might say.
Step 3: Iterative Design & Development with Agility
With features in hand, we move from concept to code using a highly agile development process. With short, focused sprints, our dedicated teams design, develop, and test in continuous cycles, ensuring seamless integration and top performance.
As an MVP app development company, we prioritize open communication through regular client feedback loops, keeping you continually informed and involved. We're agile, so we can pivot quickly to respond to new information or changing priorities. We utilize our expertise in various technologies to develop your MVP on a stable and scalable platform. That means it can grow and adapt as your product does.
Step 4: Launch, Learn, and Iterate
We don’t disappear after launch. That’s when some of the most valuable work begins. We help integrate analytics tools, track product usage, and collect real user feedback from day one.
Whether it’s A/B testing, refining features, or planning your next sprint, we stay engaged to help you learn fast and scale smart. Our goal is not just to build your MVP — it’s to help you turn it into a sustainable, growing product.
Understanding how to build an MVP strategically is the first step towards transforming your innovative concept into a market-ready product with real traction. Still, the success depends not only on what you build, but who you build it with. A reliable development partner brings more than technical skills — they bring strategic insight, startup experience, and a shared commitment to your product’s growth.
How Much Does MVP Development Cost?
The cost of developing an MVP depends on several factors, including the complexity of your product, the number of features, design requirements, and your chosen technology stack. On average, early-stage startups should expect to invest between $20,000 and $70,000 for a professionally developed MVP. Projects on the lower end tend to focus on a single user flow or problem, while those on the higher end may include more advanced features, custom integrations, or scalability requirements from day one.
We always start with a product discovery service to define the essential features needed to deliver value and validate your core assumptions. This helps avoid wasting resources on unnecessary functionality and ensures your budget is used efficiently. We also work in Agile sprints, which allows us to iterate quickly, gather early feedback, and adjust the scope based on evolving needs—all while maintaining full transparency around timelines and costs.
The bottom line? Your MVP doesn’t have to be expensive, but it does need to be focused. Our goal is to help startups launch a lean, testable product that delivers real user value without breaking the bank—and gives you a solid foundation to grow from.
Final Words About Startup MVP Development
An MVP isn’t about doing less — it’s about learning faster. It’s your startup’s best chance to test assumptions, engage real users, and move forward with clarity and confidence. When done right, an MVP is not a shortcut — it’s a strategic investment that helps you avoid costly mistakes and focus your resources where they matter most.
If you have a product idea and want to validate it the smart way, our team is here to help. We have over a decade of experience in building MVPs for startup companies, and already know all the ins and outs of the process. Even if you're still shaping your concept, we’d be happy to talk. Contact us to discuss what your MVP could look like and how to make it work.
FAQ about MVP Development for Startups
Can an MVP include both a mobile app and a web platform?
While possible, for a true MVP, it's often more strategic to focus on one primary platform first (e.g., mobile-first or web-first) where your target users are most concentrated. This helps maintain the "minimum" scope, accelerates launch, and allows you to gather focused feedback before expanding.
How long does it typically take to build an MVP?
The timeline varies significantly based on complexity, but most focused MVPs can be developed and launched within 3 to 6 months. The key is strict feature prioritization and agile methodologies to ensure rapid delivery of core functionality. If you cooperate with an experienced startup MVP development agency, it can also help you speed up the process, as the experts already know how to avoid common pitfalls.
What's the difference between an MVP and a prototype?
A prototype is a non-functional or partially functional model used for testing concepts and user flows, typically before any significant development. An MVP, on the other hand, is a fully functional, market-ready product that delivers core value to real users and is designed for actual launch and validation.
Overcoming challenges in securing investments and fostering growth is paramount for startup founders on their entrepreneurial journey. Access our whitepaper on "Business models and pricing" to have the opportunity to unveil the hidden potential of your next startup idea.
 Read the full case study
Read the full case study
 Read the full case study
Read the full case study